SQL IN ACTION
整理SQL的日常用法
依旧还是SQL,毕竟真正工作中最常用的东西,上一篇主要说了些原理性质的东西,这篇写一些常用或者少见的HQL、Spark SQL、Oracle SQL的用法,碰到不熟的,就记录下,方便以后查阅,更新ING。
1.Hive SQL
1. grouping sets
会把所有grouping的字段(key)都单独累计一次,组合key的话,没有的key显示null,比如:可以在求汇总行的时候用来代替 union 或者 union all。
demo:
根据pro_id,获取uv,且pro_id为’ALL’代表全部;
--去除null
select
case
when r2.pro_id is not null then r2.pro_id
else r2. pro_all_name
end as pro_id,
r2.uv
from
(
--获取带null的结果
select
r1.pro_id,
'ALL' as pro_all_name,
count(distinct r1.user_id) as uv
from
(
--获取基础数据
select
pro_id,
day,
user_id
from
pro_user_df
order by
day asc
) r1
group by
r1.pro_id,
'ALL' GROUPING SETS (r1.pro_id, 'ALL')
) r2
2. 窗口函数(含grouping sets)
(详情可参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/9fda829b1ef1?from=timeline)
窗口函数,对一定窗口期内的数据进行聚合;
** 可以为:sum(), min(),max(),avg()等;
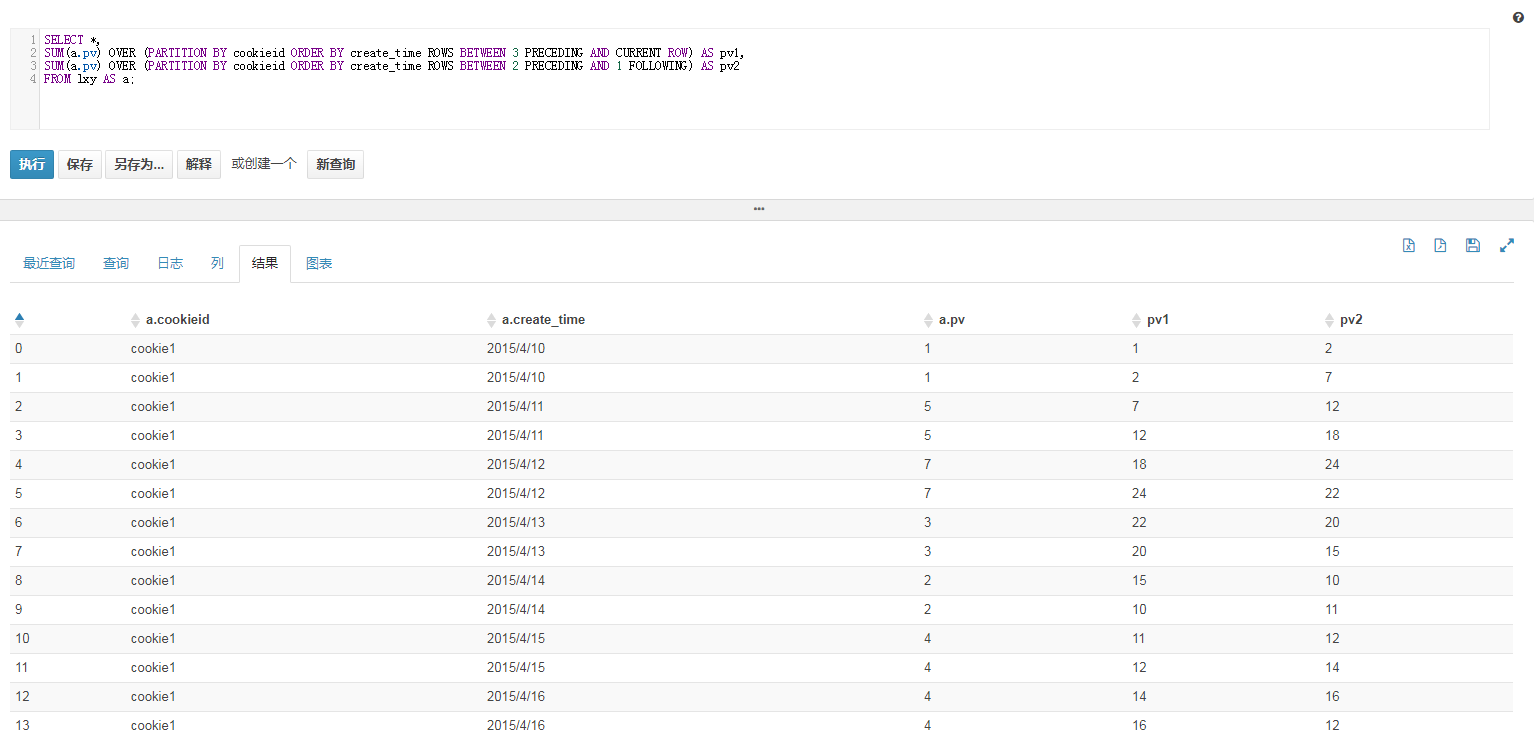
假设有三个字段,cookieid、create_time、pv;
select *,
sum(a.pv) over (partition by cookieid order by create_time
rows between 3 preceding and current row) as pv1,
sum(a.pv) over (partition by cookieid order by create_time
rows between 2 preceding and 1 following) as pv2
from lxy as a;
在这里根据cookieid进行分组,然后按照create_time进行分组,选择不同的窗口进行一定函数的聚合运算。 基本的语法是rows between 一个时间点 and 一个时间点
时间点分别可以是以当前行作为参考系,前面几行n preceding或者是后面几行n following,也可以是当前行current row。总之就是决定你聚合前多少行到多少行,类似一个滑动窗口,参考下图。
新增加序号列ntile, row_number(), rank(), dense_rank();
demo:
select *,
ntile(3) over (partition by cookid2 order by pv) as n1,
row_number() over (partition by cookid2 order by pv) as n2,
rank() over (partition by cookid2 order by pv) as n3,
dense_rank() over (partition by cookid2 order by pv) as n4
from lxy3;
结果:
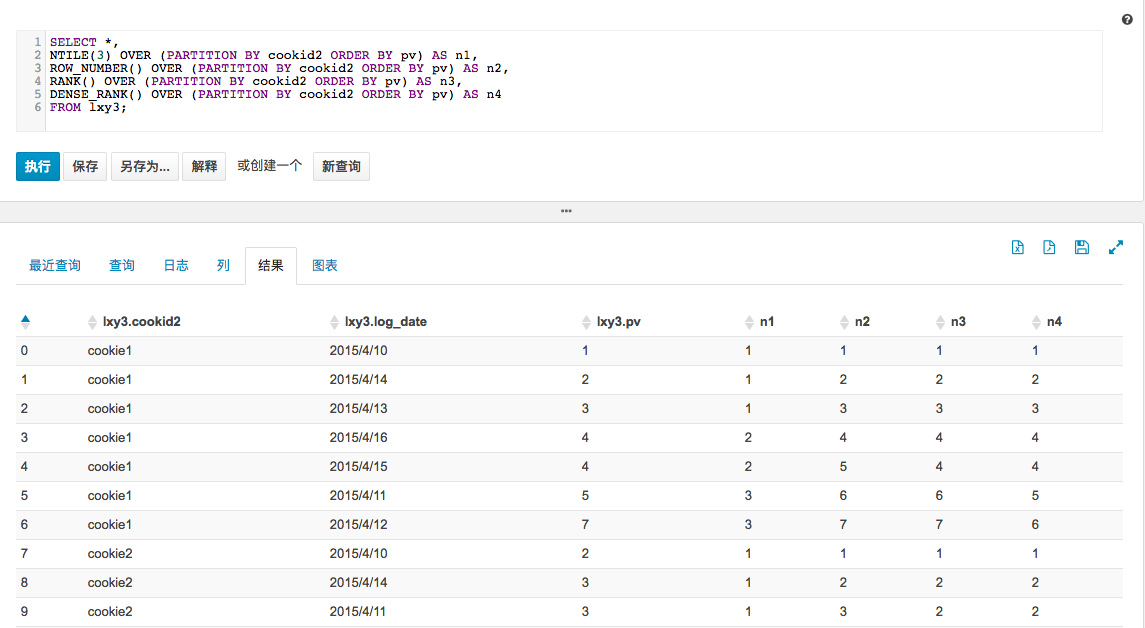
可以看到,对于ntile函数,传入的参数n是指要切分成多少份,返回对应的序号(如果切片不均匀,默认增加第一个切片的分布),row_number()则是生成一列连续的序号,rank()与row_number()类似,只是对于数值相同的这一项会同时为相同的序号,下一个序号跳过,比如倒数第二列当中有出现4,4,6没有5;而dense_rank()则相反,会紧跟着下一个是紧接着的序号,比如4,4,5。后面三个类似,只是对于相同情况区分不同。
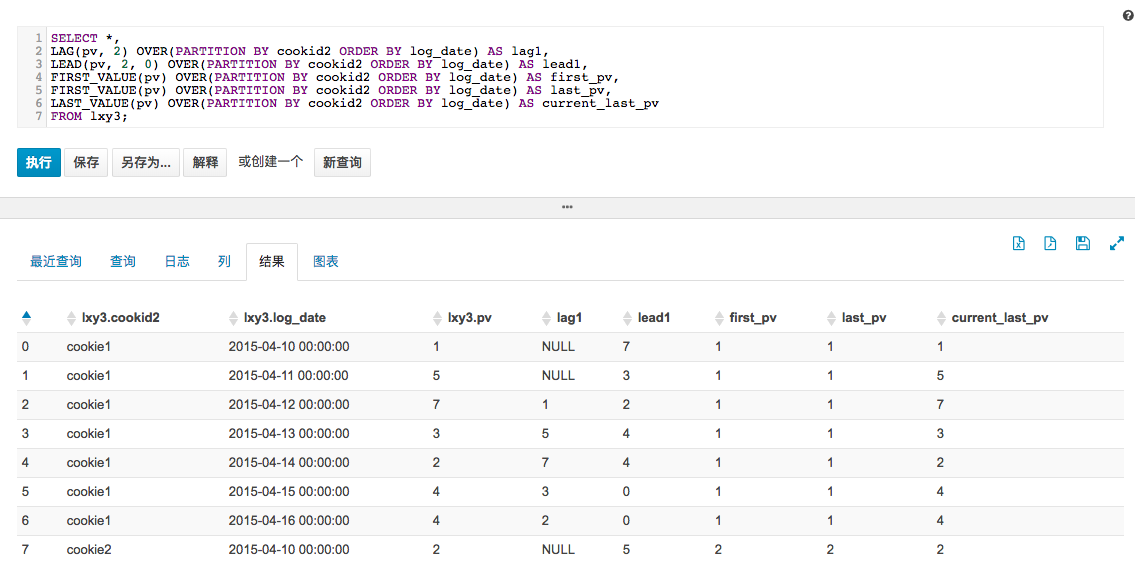
lag,lead,first_value,last_value
这几个函数可以通过字面意思记得,lag是迟滞的意思,也就是对某一列进行往后错行;lead是lag的反义词,也就是对某一列进行提前几行;first_value是对该列到目前为止的首个值,而last_value是到目前行为止的最后一个值。
demo:
select *,
lag(pv, 2) over(partition by cookid2 order by log_date) as lag1,
lead(pv, 2, 0) over(partition by cookid2 order by log_date) as lead1,
first_value() over(partition by cookid2 order by log_date) as first_pv,
first_value() over(partition by cookid2 order by log_date) as last_pv,
last_value() over(partition by cookid2 order by log_date) as current_last_pv
from lxy3;
结果:
grouping set, cube, roll up
数据demo:
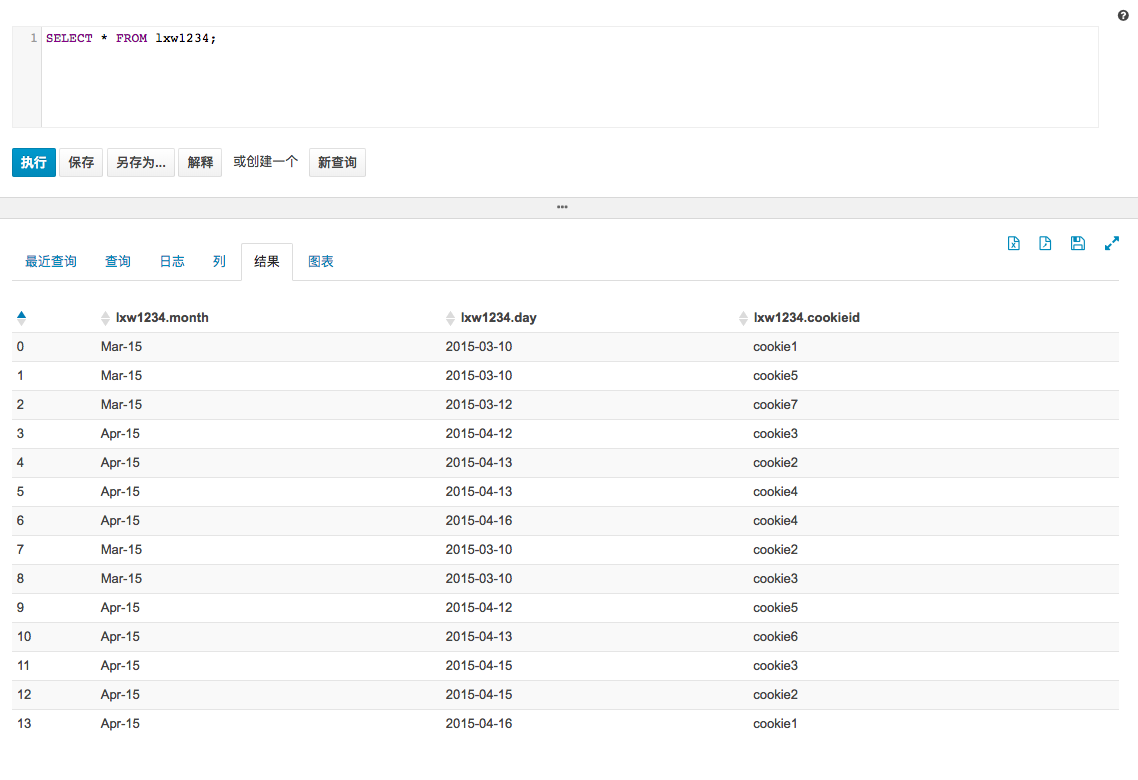
sql:
select month,
day,
count(distinct cookieid) as count_id,
grouping__id
from lxw1234
group by month, day
grouping sets(month, day)
order by grouping__id;
结果:
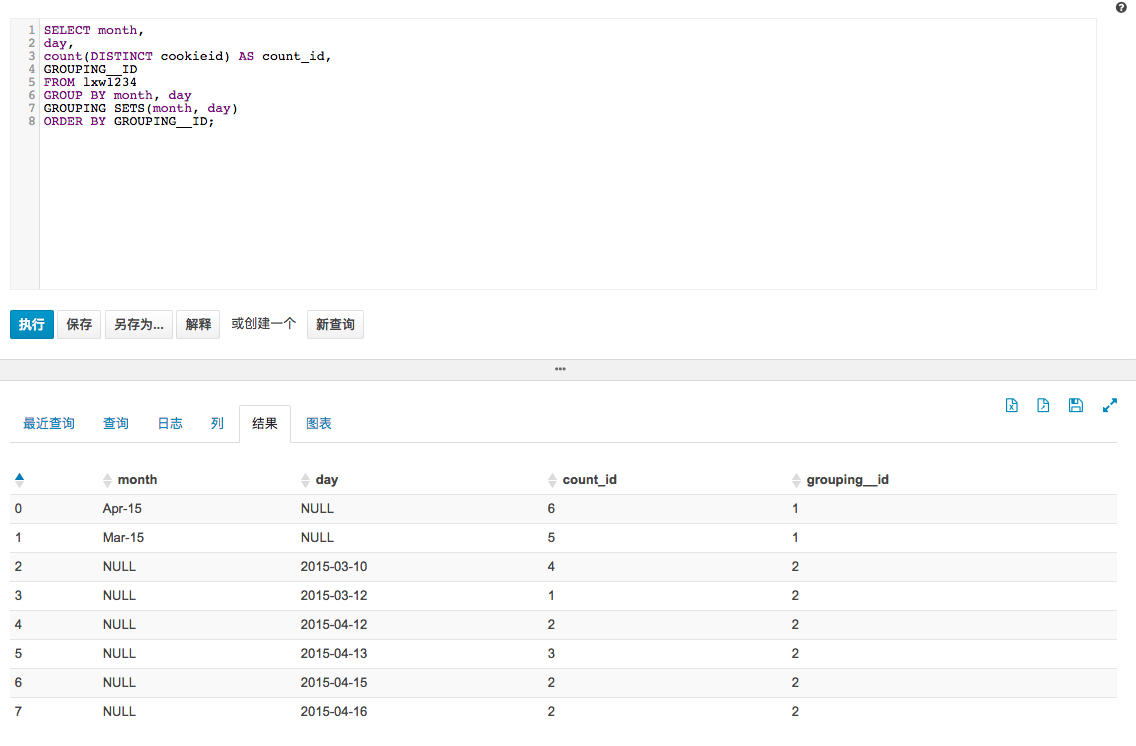
1.grouping_id是自动生成的,是进行了grouping_set()的操作之后。
2.下划线有两个
3.需要先做group by操作再传入grouping sets
4.等价于先group再union all的做法
cube就是比以上的grouping sets多了一个两列的整合,也就是笛卡尔乘积
sql:
select month,
day,
count(distinct cookieid) as count_id,
grouping__id
from lxw1234
group by month, day
with cube
order by grouping__id;
结果:
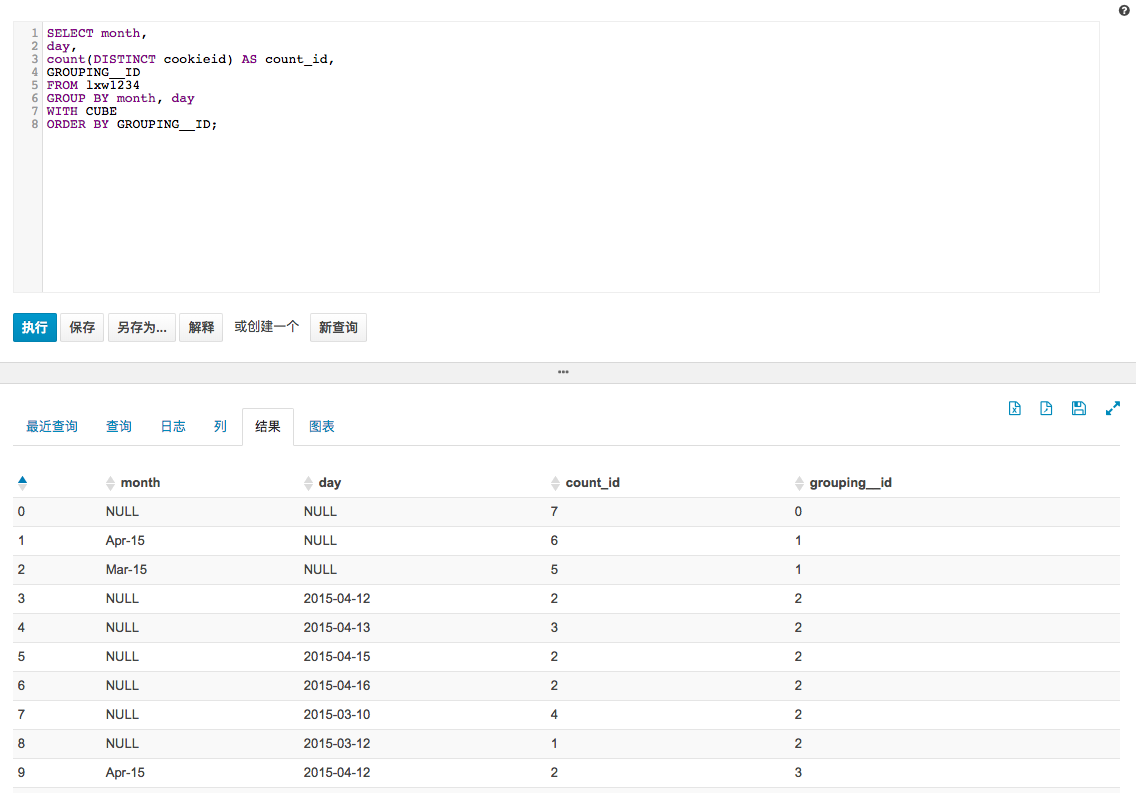
把cube改成roll up
sql:
select month,
day,
count(distinct cookieid) as count_id,
grouping__id
from lxw1234
group by month, day
with rollup
order by grouping__id;
结果:
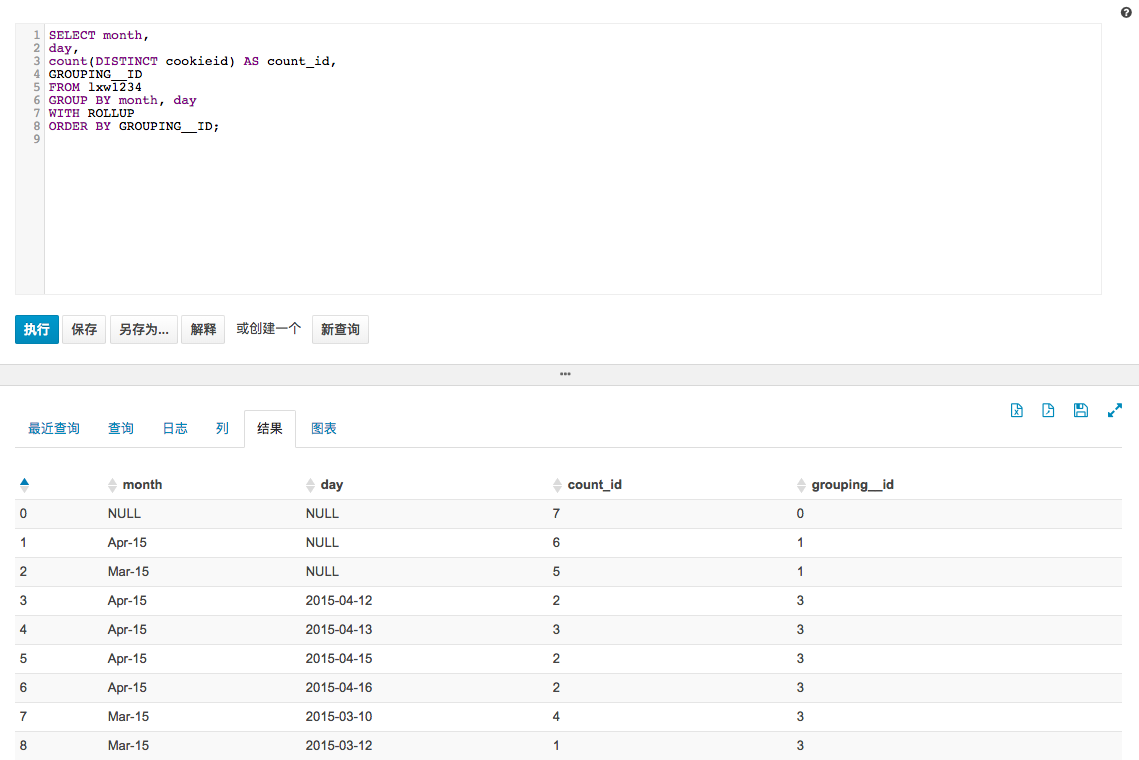
可以看到,这个时候就不会返回以右边为关键字的聚合结果,只是返回左边的键以及笛卡尔乘积的结果。
month, day换顺序结果:

所以,关键字的顺序对rollup的结果也是有影响的。
cume_dist
计算某个窗口或分区中某个值的累积分布。假定升序排序,则使用以下公式确定累积分布:
小于等于当前值x的行数 / 窗口或partition分区内的总行数。其中,x 等于 order by 子句中指定的列的当前行中的值。
demo:
select studentId,math,departmentId,classId,
-- 统计小于等于当前分数的人数占总人数的比例
cume_dist() over(order by math) as cume_dist1,
-- 统计大于等于当前分数的人数占总人数的比例
cume_dist() over(order by math desc) as cume_dist2,
-- 统计分区内小于等于当前分数的人数占总人数的比例
cume_dist() over(partition by classId order by math) as cume_dist3
from student_scores where departmentId='department1';
结果
studentid math departmentid classid cume_dist1 cume_dist2 cume_dist3
111 69 department1 class1 0.1111111111111111 1.0 0.2
113 74 department1 class1 0.4444444444444444 0.7777777777777778 0.4
112 80 department1 class1 0.6666666666666666 0.4444444444444444 0.6
115 93 department1 class1 0.8888888888888888 0.2222222222222222 0.8
114 94 department1 class1 1.0 0.1111111111111111 1.0
124 70 department1 class2 0.2222222222222222 0.8888888888888888 0.25
121 74 department1 class2 0.4444444444444444 0.7777777777777778 0.5
123 78 department1 class2 0.5555555555555556 0.5555555555555556 0.75
122 86 department1 class2 0.7777777777777778 0.3333333333333333 1.0
结果解释:
第三行:
cume_dist1=小于等于80的人数为6/总人数9=0.6666666666666666
cume_dist2=大于等于80的人数为4/总人数9=0.4444444444444444
cume_dist3=分区内小于等于80的人数为3/分区内总人数5=0.6
percent_rank
计算给定行的百分比排名。可以用来计算超过了百分之多少的人。
(当前行的rank值-1)/(分组内的总行数-1)
demo:
select studentid,departmentid,classid,math,
row_number() over(partition by departmentid,classid order by math) as row_number,
percent_rank() over(partition by departmentid,classid order by math) as percent_rank
from student_scores;
结果
studentid departmentid classid math row_number percent_rank
111 department1 class1 69 1 0.0
113 department1 class1 74 2 0.25
112 department1 class1 80 3 0.5
115 department1 class1 93 4 0.75
114 department1 class1 94 5 1.0
124 department1 class2 70 1 0.0
121 department1 class2 74 2 0.3333333333333333
123 department1 class2 78 3 0.6666666666666666
122 department1 class2 86 4 1.0
216 department2 class1 74 1 0.0
215 department2 class1 82 2 0.2
212 department2 class1 83 3 0.4
211 department2 class1 93 4 0.6
213 department2 class1 94 5 0.8
214 department2 class1 94 6 0.8
223 department2 class2 74 1 0.0
222 department2 class2 78 2 0.25
224 department2 class2 80 3 0.5
225 department2 class2 85 4 0.75
221 department2 class2 99 5 1.0
结果解释:
studentid=115,percent_rank=(4-1)/(5-1)=0.75
studentid=123,percent_rank=(3-1)/(4-1)=0.6666666666666666
3. hive 行列转换操作
先参考下面链接,有空再整出来:
https://www.cnblogs.com/blogyuhan/p/9274784.html
4. hive 常用字符串操作
1.concat,concat_ws,collect_set,collect_list
(参考列转行)
collect_set:collect_set(col)函数只接受基本数据类型,
主要作用是将某字段的值进行去重汇总,产生array类型字段。
collect_list:与collect_set相似,不去重。
concat_ws:表示concat with separator,即有分隔符的字符串连接,
concat_ws(',',collect_set(key)) 用','来连接collect_set返回的array中的每个元素。
concat:可以连接一个或者多个字符串,select concat(‘11’,’22’,’33’,‘44’);//11223344
demo:
select user_id,
concat_ws(',',collect_list(order_id)) as order_value
from col_lie
group by user_id
2.hive lateral view,explode
(参考行转列)
demo:
select user_id,
order_value,
order_id
from lie_col
lateral view explode(split(order_value,',')) num as order_id
explode:转化 array 为列
demo:
goods_id sale_info
1,2,3 aa
select explode(split(goods_id,',')) as goods_id from test;
结果为:
goods_id
1
2
3
lateral view:侧视图的意义是配合explode(或者其他的UDTF),
一个语句生成把单行数据拆解成多行后的数据结果集。
demo:
select goods_id,sale_info from test
LATERAL VIEW explode(split(goods_id,','))goods as goods_id;
结果为:
goods_id sale_info
1 aa
2 aa
3 aa
其中,LATERAL VIEW explode(split(goods_id,','))goods相当于一个虚拟表,
与原表test笛卡尔积关联。
3.split
demo:
split('a,b,c,d',',') 结果为 ["a","b","c","d"]
split('a,b,c,d',',')[0] 结果为 a
split('192.168.0.1','\\.') 结果为 ["192","168","0","1"]
4.regexp_replace(字段,原字符,新字符)
name
a123
a124
regexp_replace(name,'a','')
结果为:
123
124